How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, whether for recreational purposes, professional applications, or simply satisfying curiosity. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding fundamental components and regulations to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial footage. We will cover everything from pre-flight checks and safety procedures to troubleshooting common issues and maintaining your drone for optimal performance.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation, leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and confidence to operate your drone responsibly and proficiently. We will explore the legal landscape surrounding drone usage, provide step-by-step instructions for various flight maneuvers, and offer insights into enhancing your aerial photography and videography skills. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how to navigate the skies safely and creatively.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and prioritizing safety. Failure to do so can result in fines, accidents, and legal repercussions. This section Artikels crucial aspects of safe and legal drone operation.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Drone regulations vary significantly depending on location (urban, rural, near airports). Urban areas often have stricter rules regarding flight altitudes and proximity to buildings and people. Rural areas may have more relaxed regulations, but always check local ordinances. Airports have strict no-fly zones due to safety concerns. Before flying, always consult the relevant aviation authority in your region (e.g., the FAA in the USA, CAA in the UK) for specific regulations and airspace restrictions.
Registering your drone is often mandatory, and obtaining necessary permits might be required for commercial operations or flights in specific areas.
Drone Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation involves a structured approach encompassing pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight procedures. This ensures both the drone’s and others’ safety.
- Pre-flight: Conduct a thorough pre-flight checklist (detailed below), ensuring battery is charged, GPS signal is acquired, and software is updated. Check weather conditions – avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
- In-flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times. Avoid flying near people, animals, or structures. Be aware of airspace restrictions. Use appropriate flight modes based on your skill level and environment.
- Post-flight: Safely land the drone in a designated area. Power off the drone and store it securely. Review flight logs and footage. Inspect the drone for any damage.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist minimizes risks and ensures smooth operation.
| Item | Check |
|---|---|
| Battery Charge | Sufficient charge for the planned flight time |
| Propellers | Securely attached and undamaged |
| GPS Signal | Strong and stable signal acquired |
| Software Updates | Firmware and app updated to the latest version |
| Sensors | Clean and functioning correctly |
| Flight Controller | Properly calibrated |
| Weather Conditions | Suitable for flight |
| Airspace Restrictions | No restrictions in the planned flight area |
Drone Safety Briefing for New Operators
A safety briefing should emphasize responsible drone operation, including legal compliance, pre-flight checks, emergency procedures, and respect for others’ safety and privacy.
- Review local drone regulations.
- Explain the importance of pre-flight checks.
- Demonstrate safe takeoff, hovering, and landing procedures.
- Discuss emergency procedures (e.g., loss of signal, battery failure).
- Emphasize maintaining visual line of sight.
- Explain privacy concerns and the importance of respecting others’ space.
Comparison of Drone Safety Features
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Return-to-Home | Automatic return to the takeoff point if signal is lost | Increased safety | Reliance on GPS signal |
| Obstacle Avoidance | Sensors detect and avoid obstacles | Reduced risk of collisions | May not detect all obstacles |
| Geofencing | Limits flight area to a predefined zone | Prevents unauthorized flights | Requires setup and configuration |
| Low Battery Warning | Alerts the operator when battery is low | Prevents unexpected power loss | Operator must respond to the warning |
Understanding Drone Components and Controls
Understanding your drone’s components and how to control it is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section provides a breakdown of key components and control mechanisms.
Drone Components and Their Functions, How to operate a drone
A typical drone comprises several key components working in concert. Understanding their roles is vital for troubleshooting and safe operation.
- Propellers: Generate thrust for flight and maneuverability.
- Motors: Drive the propellers.
- Battery: Provides power to the drone.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, responsible for stabilization, navigation, and response to pilot commands.
- Camera: Captures images and videos (varies depending on drone model).
- GPS Module: Enables precise positioning and navigation.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures orientation and movement for stabilization.
Types of Drone Controllers and Functionalities

Drone controllers vary in design and functionality, from basic joysticks to sophisticated systems with integrated screens and features. Some controllers offer adjustable sensitivity, allowing for precise control. Others incorporate additional buttons and switches for advanced functions like camera control and flight mode selection. The choice depends on the drone model and user needs.
Effects of Control Sticks on Drone Movement
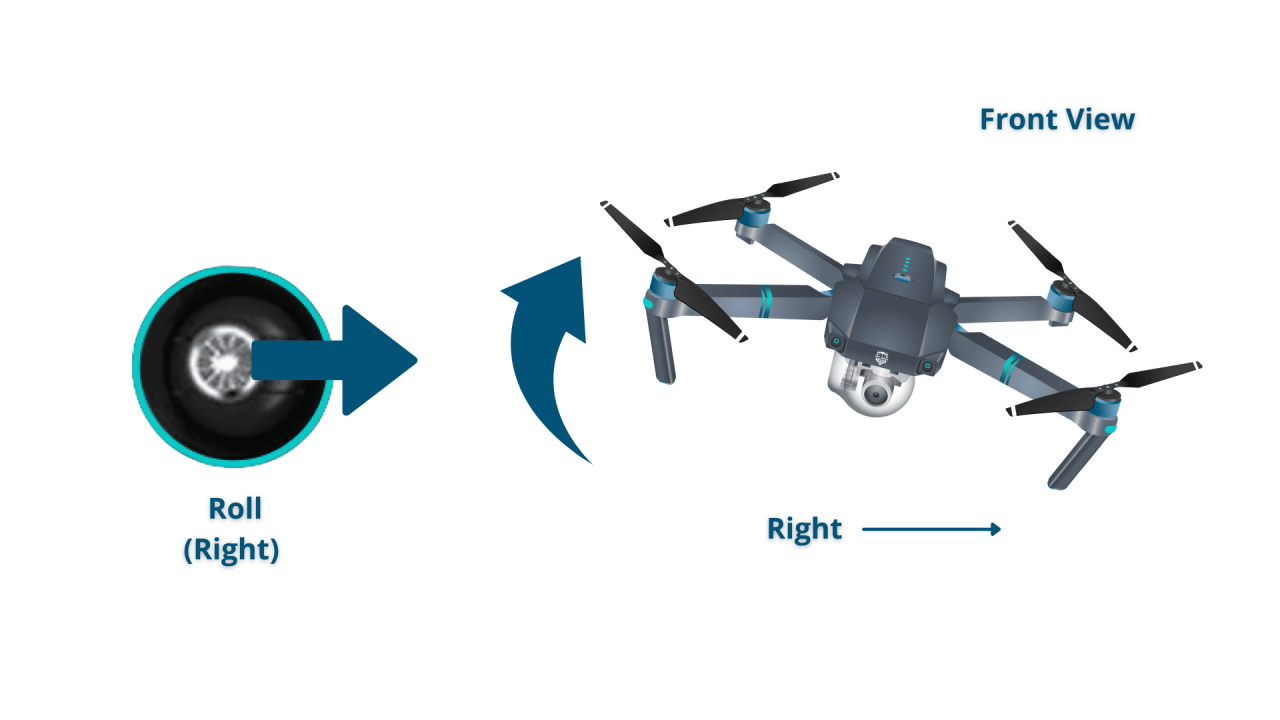
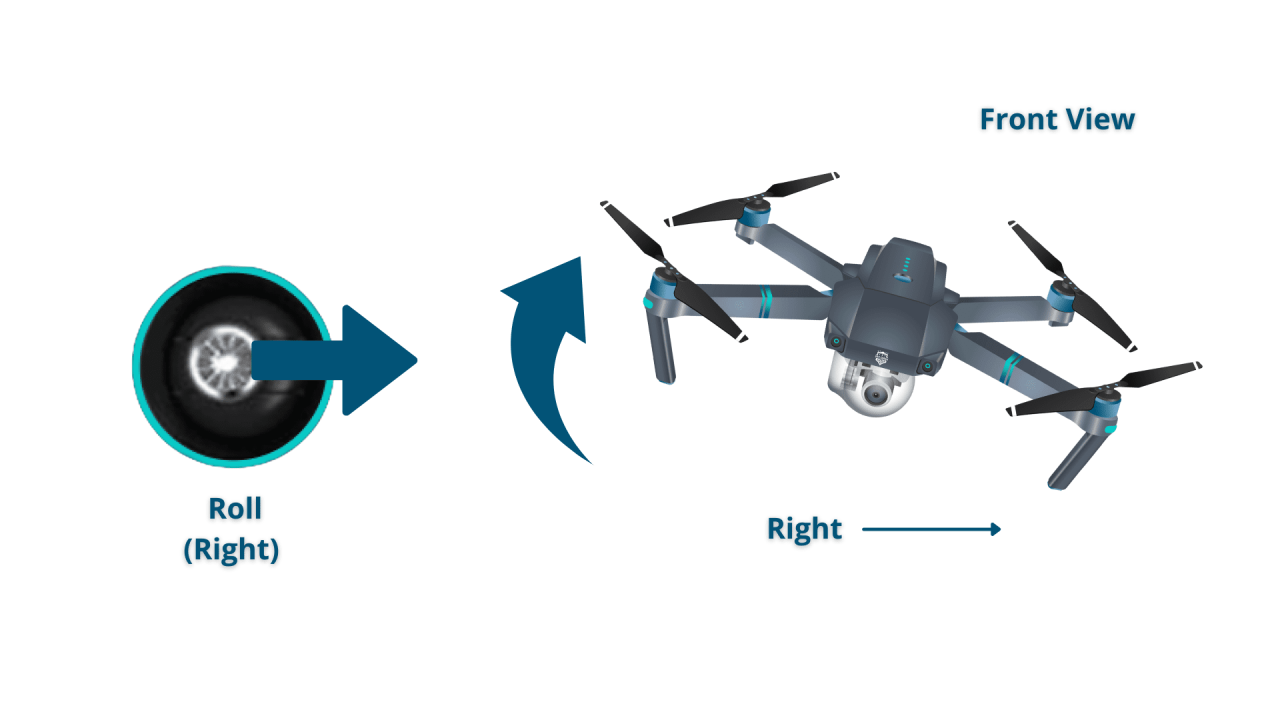
The control sticks typically control the drone’s movement in two dimensions (pitch/roll and yaw/throttle). Pushing the left stick forward usually increases forward speed, pulling it back causes backward movement. Pushing the right stick to the left causes the drone to turn left, pushing to the right causes a right turn. The vertical position of the right stick typically controls the drone’s altitude (ascending or descending).
Drone Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s sensors, especially the IMU and compass, is crucial for accurate flight and stability. The specific calibration procedure varies depending on the drone model, but generally involves following the manufacturer’s instructions. This usually involves placing the drone on a level surface and following on-screen prompts within the drone’s control app.
Connecting a Drone to its Controller
Connecting a drone to its controller usually involves establishing a radio link. Most modern drones use 2.4 GHz or 5.8 GHz radio frequencies. The process typically involves powering on the controller first, followed by the drone. The drone’s app will often guide you through the connection process. Some drones may require binding (pairing) the controller and the drone for the first time.
Pre-Flight Procedures and Setup
Thorough pre-flight preparation is essential for safe and successful drone flights. This section details the necessary steps and considerations.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A detailed checklist ensures all critical pre-flight steps are completed.
- Charge the drone’s battery to full capacity.
- Check the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Power on the controller and establish a connection with the drone.
- Verify that the GPS signal is strong and stable.
- Check for any software updates and install them if necessary.
- Inspect the drone for any damage or loose parts.
- Plan the flight path and ensure it is safe and legal.
- Review emergency procedures and know how to react in case of unexpected situations.
Selecting Appropriate Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to varying skill levels and flight conditions. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, making it easier to control. Advanced modes offer greater control and maneuverability but require more experience.
Planning a Drone Flight Path
Planning a flight path involves considering factors such as obstacles, airspace restrictions, and the desired shots. Using flight planning software can be beneficial for complex flights.
Pre-Flight Sequence Flowchart
A flowchart visually represents the sequential steps involved in the pre-flight process, ensuring a methodical and comprehensive approach.
(Note: A visual flowchart would be included here in a real article. This text description provides the logical flow): Power on Controller -> Connect to Drone -> Check Battery -> Check GPS Signal -> Check Software Updates -> Inspect Drone -> Plan Flight Path -> Check Weather -> Begin Flight
Common Pre-Flight Errors and Solutions
Identifying and addressing common pre-flight errors is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring smooth operation.
- Low Battery: Fully charge the battery before each flight.
- Weak GPS Signal: Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky.
- Software Issues: Install the latest software updates.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers.
- Improper Calibration: Recalibrate the drone’s sensors.
Basic Flight Operations and Maneuvers
Mastering basic flight operations is the foundation for more advanced maneuvers. This section Artikels the steps involved in safe takeoff, hovering, and landing, along with basic flight controls.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
Safe takeoff involves gradually increasing throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Hovering requires precise control of the throttle to maintain a stable position. Landing involves gradually decreasing throttle until the drone gently touches down.
Flight Modes (Beginner/Advanced)
Beginner mode typically restricts speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning. Advanced modes unlock full speed and maneuverability, requiring more skill and experience.
Ascending, Descending, Turning, and Lateral Movement
These maneuvers are controlled using the joysticks on the controller. Precise control comes with practice and understanding the relationship between joystick inputs and drone movements.
Precise Drone Control Techniques
Techniques for precise control involve understanding the drone’s responsiveness and using small, incremental joystick movements. Practice is crucial for developing smooth and controlled maneuvers.
Common Mistakes During Basic Flight Operations
Common mistakes include abrupt movements, ignoring battery levels, and losing visual contact with the drone. Solutions involve practicing smooth control, regularly monitoring battery status, and maintaining visual line of sight.
Advanced Flight Techniques and Features: How To Operate A Drone
Advanced flight features enhance capabilities and allow for creative aerial photography and videography. This section explores these features and techniques.
Advanced Flight Features (Waypoint Navigation, Return-to-Home, Follow-Me)
Waypoint navigation allows pre-programming a flight path, enabling automated flights. Return-to-home automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point if signal is lost or the battery is low. Follow-me mode keeps the drone following a designated subject.
Camera Angles and Settings

Adjusting camera angles and settings (aperture, shutter speed, ISO) is crucial for optimal image quality. Different angles and compositions create compelling visuals.
Creative Flight Maneuvers
Creative maneuvers involve combining basic and advanced controls to capture unique perspectives. Examples include orbiting a subject, flying through narrow spaces, and performing smooth camera movements.
Flight Plan Incorporating Advanced Features
A flight plan for aerial photography might involve using waypoint navigation to cover a landscape, employing follow-me mode for tracking a moving subject, and adjusting camera angles for optimal shots.
Comparison of Drone Flight Controllers
| Controller | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controller A | GPS, Return-to-Home, Waypoint Navigation | Easy to use, reliable | Limited customization options |
| Controller B | GPS, Obstacle Avoidance, Follow-Me | Advanced features, precise control | More complex to learn |
| Controller C | Basic controls, simple interface | Affordable, beginner-friendly | Limited features |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring reliable performance. This section covers key aspects of drone care and problem-solving.
Routine Maintenance Procedures
Routine maintenance includes cleaning the drone body and propellers, inspecting for damage, storing the drone in a dry place, and regularly updating the software.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failure, and software glitches. Causes can range from user error to component failure.
Troubleshooting Steps for Common Issues
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking components, reviewing flight logs, and consulting the manufacturer’s documentation. For complex issues, seeking professional help might be necessary.
Tips for Extending Drone Lifespan
Proper storage, regular cleaning, and careful handling significantly extend a drone’s lifespan.
Resources for Obtaining Drone Parts and Repairs
Many online retailers and specialized drone repair shops offer parts and repair services. The manufacturer’s website is a good starting point for finding authorized repair centers.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial footage requires understanding camera settings and employing effective filming techniques. This section covers essential aspects of drone photography and videography.
Techniques for Achieving Stable Shots
Stable shots require smooth, controlled movements and the use of appropriate flight modes. Using features like gimbal stabilization further enhances image stability.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Understanding aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for controlling exposure, depth of field, and image sharpness. Experimentation and practice are key to mastering these settings.
Camera Angles and Compositions for Compelling Visuals
Different angles and compositions create diverse perspectives and enhance visual storytelling. Experimenting with various angles, like bird’s-eye views, low-angle shots, and tracking shots, adds visual interest.
Editing Drone Footage
Editing involves using video editing software to enhance footage, correct color, add music, and create a polished final product.
Guide to Achieving Professional-Looking Aerial Photography
Achieving professional-looking results involves careful planning, precise execution, and post-processing techniques. Combining good composition, proper lighting, and effective editing leads to high-quality aerial photography and videography.
Mastering drone operation is a journey that combines theoretical knowledge with practical experience. This guide has provided a foundation for safe and responsible drone piloting, covering essential aspects from regulations and safety to advanced flight techniques and maintenance. Remember that consistent practice and adherence to safety protocols are paramount. As you gain experience, explore the creative possibilities of aerial photography and videography, always respecting airspace regulations and prioritizing safety above all else.
Happy flying!
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires knowledge of regulations and safe practices. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including legal considerations and practical tips, you should check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Proper training and understanding are crucial for responsible drone piloting.
Helpful Answers
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with features like GPS stabilization and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Research models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations, but generally, charge after each flight and avoid completely depleting the battery to extend its lifespan.
What do I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If it doesn’t automatically activate, carefully bring the drone down using manual control. Ensure you are in a location with a clear view of the sky.
How do I obtain necessary permits or licenses for drone operation?
Regulations vary by location. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific requirements and licensing procedures in your area.